Pigmentation Causes
What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation is primarily influenced by melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes within the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Melanin is responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. The amount and distribution of melanin in the skin determine its shade, ranging from very light to very dark.
The key factors that contribute to skin pigmentation are:
- Genetics: The most significant factor in determining an individual’s skin color is their genetic makeup. Genes inherited from parents play a crucial role in determining the amount and type of melanin produced by melanocytes.
- Melanin production: Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: eumelanin, which appears dark brown or black, and pheomelanin, which is more yellow to red. The relative amount and ratio of these melanins influence skin color.
- Exposure to UV radiation: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin as a protective response. This is why people tend to get tanned after sun exposure. However, excessive UV exposure can lead to sunburn and other skin issues.
- Hormones: Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, can affect melanin production and distribution, leading to conditions like melasma (dark patches on the skin).
- Age: As we age, the production of melanin can decrease, leading to lighter skin in some individuals.
- Inflammatory conditions: Certain skin conditions or injuries, such as acne, eczema, or cuts, can cause temporary or permanent changes in skin pigmentation.
- Medical conditions: Some medical conditions, like vitiligo (loss of melanocytes in certain areas), albinism (complete absence of melanin), or hyperpigmentation disorders, can cause abnormal skin pigmentation.
- Ethnicity: Different ethnic backgrounds have varying levels of melanin production, resulting in diverse skin colors and tones.
It is essential to note that a combination of these factors can influence skin pigmentation and can vary significantly among individuals and ethnic groups. If you have concerns about your skin pigmentation or notice any unusual changes, it is recommended to consult with the Best Dermatologist in Kolkata for proper evaluation and advice. Additionally, maintaining sun protection and avoiding excessive UV exposure can help keep the skin healthy and prevent unwanted changes in pigmentation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Skin Pigmentation
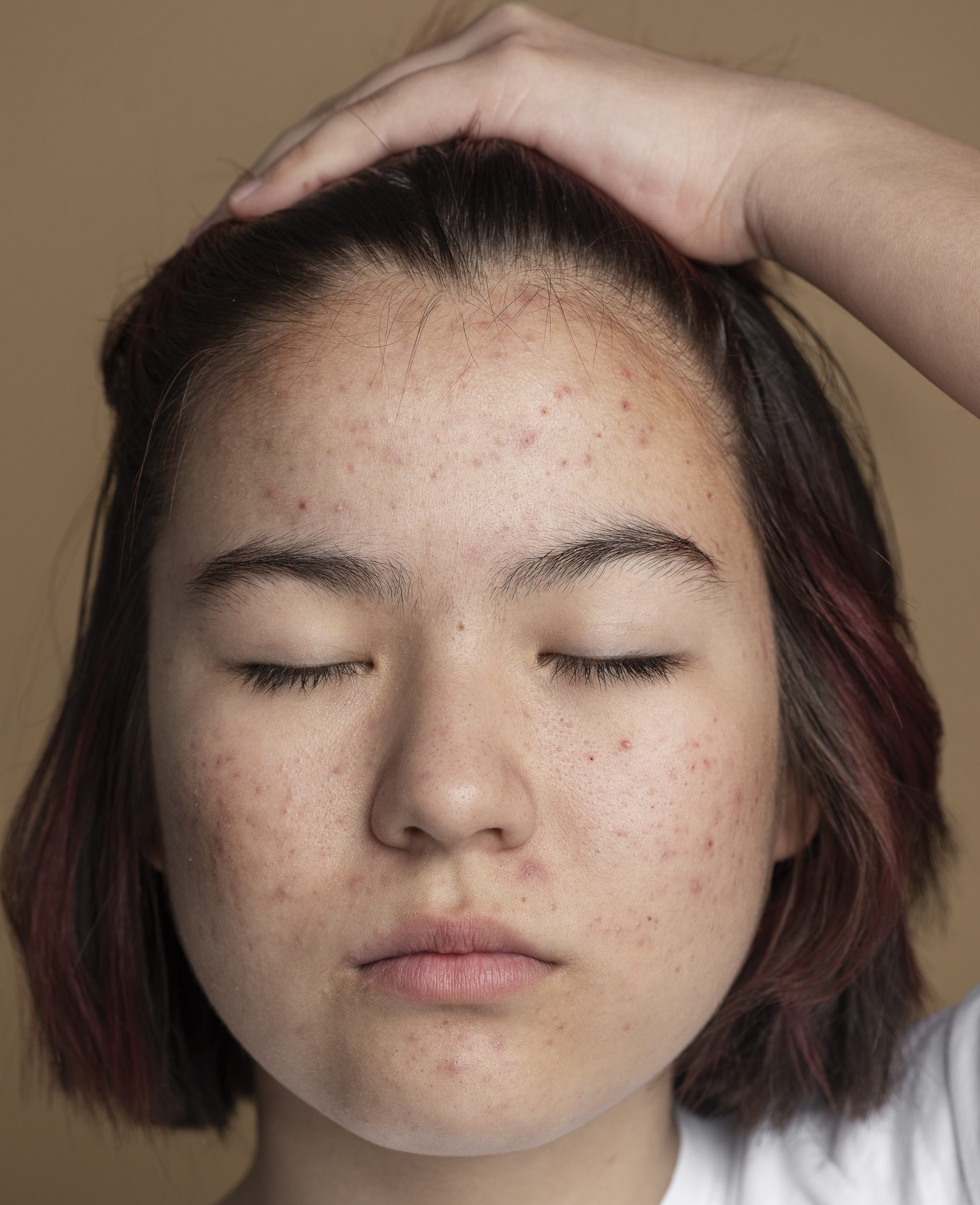
Skin pigmentation symptoms manifest as changes in skin coloration, characterized by the appearance of discolored patches on specific areas of the skin. These patches can range in color from brown to black and tend to darken when exposed to sunlight. Common types of pigmentation include:
- Freckles: Freckles are a prevalent form of skin pigmentation that develops as a result of frequent sun exposure. They typically present as small, circular spots on areas exposed to the sun, such as the face. Freckles are more commonly found in individuals with lighter skin tones and can also be influenced by hereditary factors.
- Post-inflammatory pigmentation: This type of pigmentation occurs as a response to skin injuries, such as bruises, burns, friction, or exposure to harsh chemical treatments. Post-inflammatory pigmentation can also develop after acne breakouts, resulting in reddish, brown, or black marks on the skin.
- Melasma: Melasma is a facial pigmentation disorder that primarily affects the deeper layers of the skin. It is more commonly observed in women and appears as irregular, brown to grey patches on areas such as the cheeks, nose, and jawline.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): Sunspots, also known as solar lentigines, are well-defined pigmentation spots that form as a result of prolonged sun exposure. The degree of pigmentation varies based on the amount of melanin pigment exposed to UV rays.
Eligiblity
Who is the right candidate for Pigmentation treatment?
The right candidate for pigmentation treatment typically includes individuals who have concerns related to skin discoloration, hyperpigmentation, or dark spots. Pigmentation issues can be caused by various factors, such as sun damage, hormonal changes, aging, acne scars, or certain medical conditions.
The ideal candidate for pigmentation treatment should have realistic expectations about the results and be in good overall health. It is important to consult with a qualified dermatologist or skin care Clinic in Kolkata to determine the most suitable treatment for your specific pigmentation concerns.
Common pigmentation treatment options include:
Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter or prescription creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, kojic acid, or vitamin C can help fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
- Chemical Peels: This procedure involves applying a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layer and stimulate new skin growth, improving pigmentation issues.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments target specific pigmented areas, breaking down excess melanin and encouraging skin rejuvenation.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: Similar to lasers, IPL uses light to target pigmented areas, reducing discoloration and improving skin tone.
- Microdermabrasion: This procedure involves exfoliating the skin to remove the outer layer, which can help with mild pigmentation problems.
- Microneedling: Tiny needles are used to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production and helping to reduce pigmentation irregularities.
- Cryotherapy: This treatment uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy pigmented cells, allowing new, healthier skin to grow.
Before undergoing any pigmentation treatment, it is crucial to have a consultation with a qualified professional who can assess your skin condition, and medical history, and recommend the most appropriate treatment for your needs. Additionally, it is essential to follow the post-treatment care instructions and protect your skin from further sun damage to maintain the results.